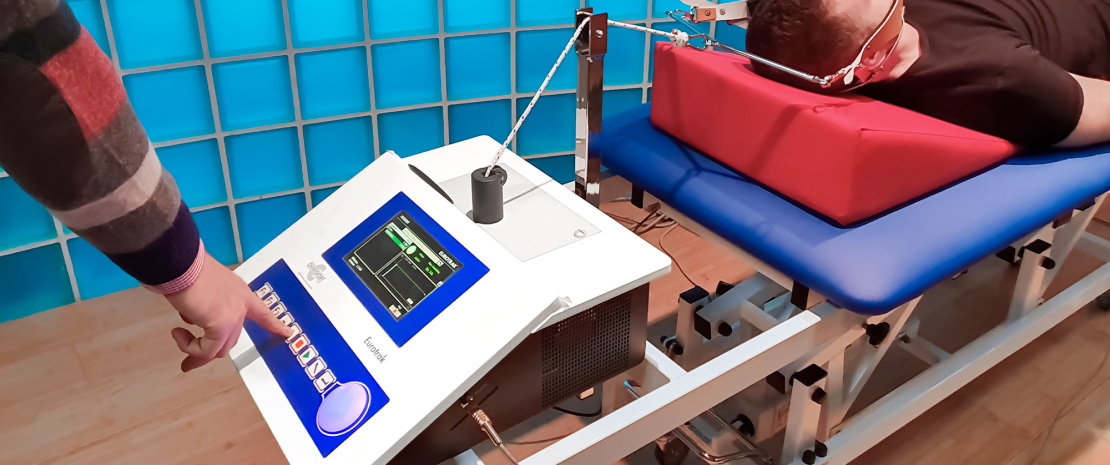

EUROTRAK traction is an innovative device made following the most sophisticated and actual technological solutions. Thanks to the large liquid crystal display (LCD) showing all functions and function keys these units can be easily and friendly used. The EUROTRAK Series Units have a microprocessor control which allows them to have important peculiarities, such as flexibility and performance, not shared by the common traction appliances available on the market.
This equipment can be used to perform lumbar and cervical tractions. Tractions can be applied in a “static”, “dynamic” or “intermittent dynamic” mode.
A series of pre-set programs aimed at specific pathologies is available, with the option of storing up to 50 personalized treatments. The display visualizes all the parameters set at a certain time and any parameter value may be modified extremely easily and quickly if required.
Throughout their treatment, patients have access to an emergency stop button to stop traction if they wish to do so.

A switch that allows you to use the traction mode cervical or lumbar is placed on the side of the device

A special remote control for stopping the treatment is held by the patient for the whole period.

The display shows all parameters set, and any parameter value may be modified extremely easily and quickly if required.
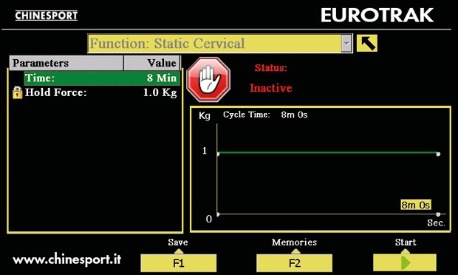
In static mode the unit delivers a steady force, equal to the set value for the whole period of the treatment. At the end of the treatment time the unit stops traction force and an intermittent sound is delivered.In order to stop the therapy before the end of the time or to stop the end sound, the therapist has to press the STOP key.
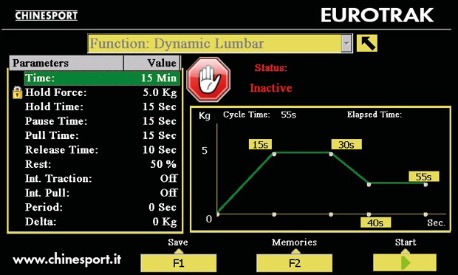
In dynamic mode there are four phases as shown in the diagram while the table gives the parameters for each phase. The therapist has always to pay attention to the patient’s feeling when the traction force is increasing.Moreover it’s important not to carry out lumbar treatment programs for cervical treatment. In lumbar mode the top force value is not bounded at 20 kg, but it can get 90 kg.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Phase 1: hold |
Hold time Hold force |
| Phase 2: pause |
Pause time Rest: percentage of the traction force one wants it is delivered during the pause time |
| Phase 3: pull |
Pull time: time to go from the set pause value to the set hold value |
| Phase 4: release |
Release time: time to go from the set hold value to the set pause value |
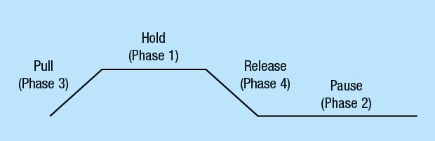
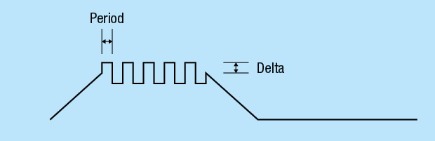
When the unit works in dynamic mode, for instance, with reference to the hold phase, the following diagram gives a description of the intermittent working. The Delta is the variation of the set force for each Period. The set Delta and Period values are good for all the phases set ON.

Introduction - The effects of spinal traction - Types of spinal traction - Continuous traction - Intermitent mechanical traction - Manual traction - Positional traction - Active Lumbar traction - Indications and contraindications - Herniated disc with protrusion - McKenzie’s extension basics - Degenerative discopathy - Articular hypomobility (Articular dysfunction) - Contraindications for spinal traction - Lumbar traction techniques - Introduction - Traction weights and body friction - A table with mobile sections - The patient must be in relax - Traction belts - Patient’s positions - Type of traction - Prone position - Protective scoliosis - Cervical traction techniques - Introduction - Traction angles - Chin strap - Traction weights - Patient in relax - Treatment duration - Temporomandibular joint - Manual cervical traction - Unilateral cervical traction - Conclusions
Brochure, Ed. July 2021, English. 56 pages.

Introduction - Vacuum therapy - WOK trolley - C.R.E.T. therapy - Shockwave therapy - Laser therapy - High intensity laser therapy - Scanning laser therapy - Low level laser therapy - Electrotherapy - Ultrasound therapy - Combined therapy - Magneto therapy - Radar therapy - Pressotherapy - Traction therapy - TENS units - Thermotherapy
Brochure, Ed. Dec. 2024, English. 60 pages.
