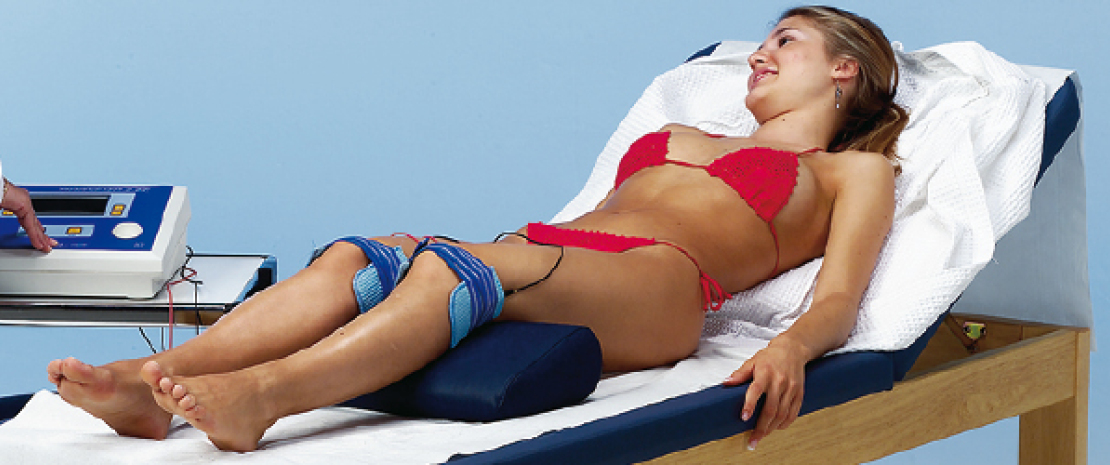
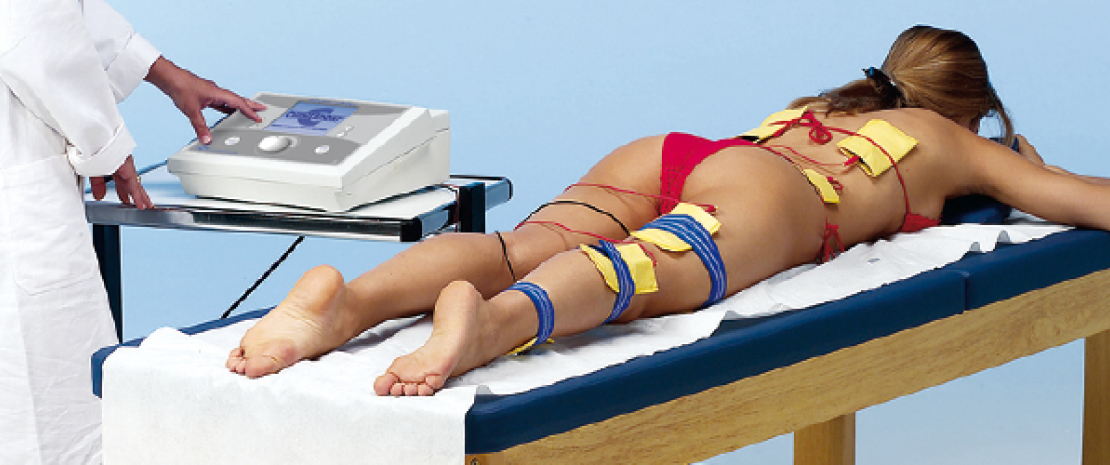

Electro therapy uses the biological effects that can be obtained using electricity for therapeutic purposes, and involves electric currents that are passed through the relevant part of the body, being careful to choose them with specific characteristics that are suitable for the purposes to be achieved. Electro therapy is used to stimulate denervated muscles, to reduce hypotrophy due to non-use of a normoinnervated muscle, and to maintain muscular trophicity of denervated or partially innervated muscles, in order to strengthen the innervated muscle.
The principal effects of electric current applied to body tissue include motory activation, thermal, trophic, analgesic, and chemical effects. Each muscular stimulation electric impulse is characterized by:
ELECTRICAL STIMULATION BENEFITS
1. relaxation of spastic muscles;
2. prevention of atrophy from disuse;
3. increased local blood circulation;
4. muscular rehabilitation;
5. immediate post surgery stimulation to the calf muscles to prevent venous thrombosis;
6. better range of movement.
You can find the description of the Basic Line, Plus Line and Excellent Line in the dedicated section.



MEDICSTIM units are a high quality devices that assures complete patient and operator safety (the unit complies with international regulations) in addition to offering numerous types of therapeutic applications.
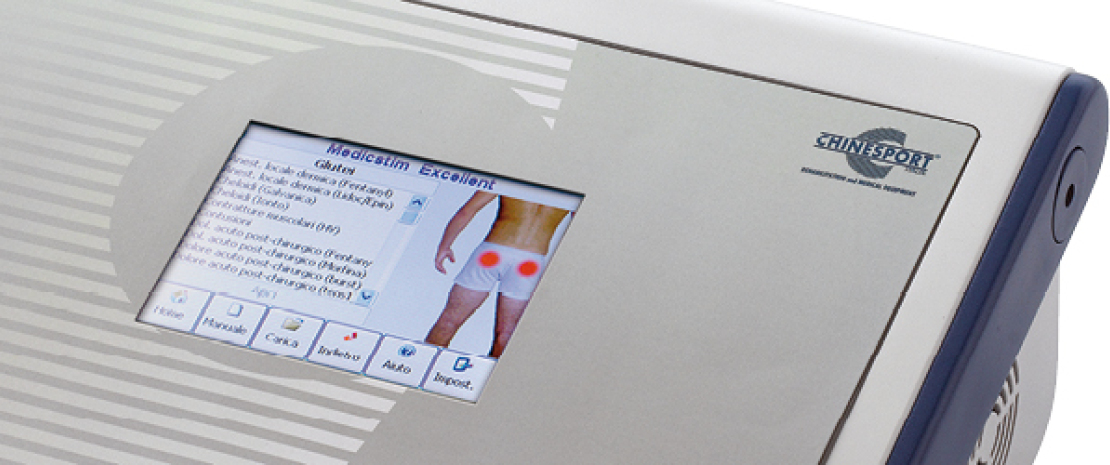
The electrotherapy units in the MEDICSTM series feature a control panel that is optimized in accordance with the specific field of application. All operating parameters are managed and controlled in real time by the user thorugh a large, backlit interface: the display shows all operational messages, the state of the unit during normal therapeutic operation, and any error messages.
Direct current
Galvanic current (or direct or continuous current) is generated by the uniform movement of electric charges in the same direction. This kind of current serves best as a trans-cutaneous carrier of medicines or cosmetically active substances.
Variable currents
Variable currents are generally meant to denote all those currents where the intensity is not constant over time. We can distinguish between low, medium, and high frequency currents, and for physiotherapy purposes, this means the following frequency ranges:
- low frequency: from 0 to 800 Hz,
- medium frequency: from 800 to 60,000 Hz,
- high frequency: over 100,000 Hz.
The different types of currents can be summarized according to their specific actions (or biological effects):
The ability to use direct current as a “carrier” to introduce substances in the ionic state into the tissues through the skin has been known for a long time. This technique has been tested and verified over time. Current thinking confirms that iontophoresis is an effective way of administering different substances when localised action is required. Actually, the percutaneous application of medicinal substances is notably affected by the barrier function of the corneal stratum.
Methods generally used to neutralise this effect are not always effective. Overcoming the cutaneous “barrier” stratum is not easy even when direct current is used, since substances generally prefer to enter via the glandular ducts and hair channels. In addition, the substances can only reach a few millimetres depth.
Excluding the cases where a localised surface effect only is required, the effectiveness and distinctiveness of iontophoresis lies in the fact that the substances introduced in this fashion seem to bind more stably with proteins that normally form part of surface tissue. The substance is therefore reabsorbed into the general cycle more slowly than it would have been if administered hypodermically.
The general effect is however linked with the type of substance used: direct current only functions as a medium. Therefore medicinal ionophoresis refers to substances introduced that have pharmalogical effects.

Introduction - Vacuum therapy - WOK trolley - C.R.E.T. therapy - Shockwave therapy - Laser therapy - High intensity laser therapy - Scanning laser therapy - Low level laser therapy - Electrotherapy - Ultrasound therapy - Combined therapy - Magneto therapy - Radar therapy - Pressotherapy - Traction therapy - TENS units - Thermotherapy
Brochure, Ed. Dec. 2024, English. 60 pages.