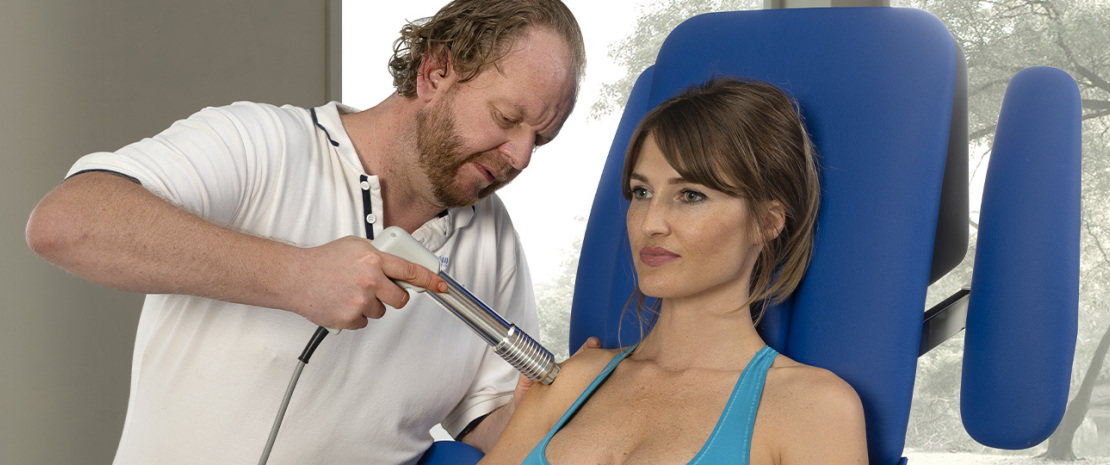


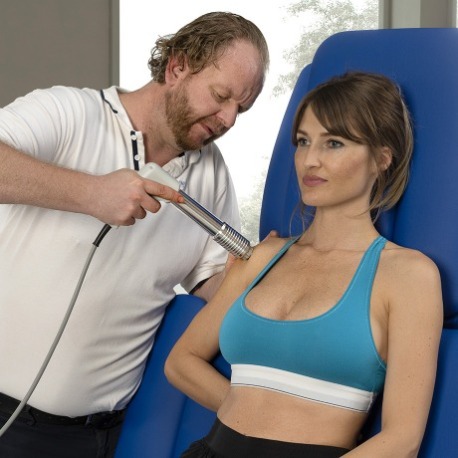
From a physical point of view shockwaves are defined as high-energy acoustic waves. Specifically, they are pressure pulses generating direct mechanical force with the aim to convey energy to body tissues in order to stimulate healing processes.
Shockwave should not be confused with ultrasound wave that is normally used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Unlike ultrasound, shockwave has a pulsed form and provide much higher pressure values, on average 1000 times higher.
It's available a trolley mounted SHOCK WAVE EXCELLENT model featured by a power up to 5 bar, or alternative a portable version called SHOCK WAVE COMPACT EXCELLENT with a power up to 4 bar. This latter model can also be used in combination on a special trolley where can be placed or removable representing another option and coded as another model.
Shockwave propagation speed, as with each acoustic wave, is particularly related to the means that conveys it and to the intensity of the shockwave.
Biological structures like cell walls, whose thickness is comparable to few molecular layers, undergo very high pressure gradients when shockwaves pass.
The mechanical properties of the biological means that are hit by the shockwave, like elastic and compressible properties, influence the transmission of shockwave determining the propagation speed.
When shockwaves pass through a fluid, they generate various pressure differences that produce gas bubbles. The next shockwave hitting these bubble generate a strong implosion that will produce liquid spilling all over the tissue to be treated. As a consequence to these lesions some biological events occur, they differ according to the hit tissue.

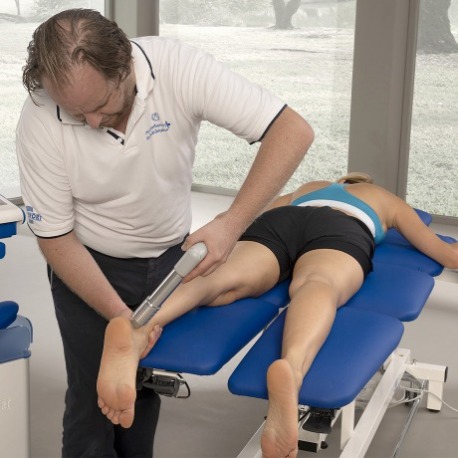
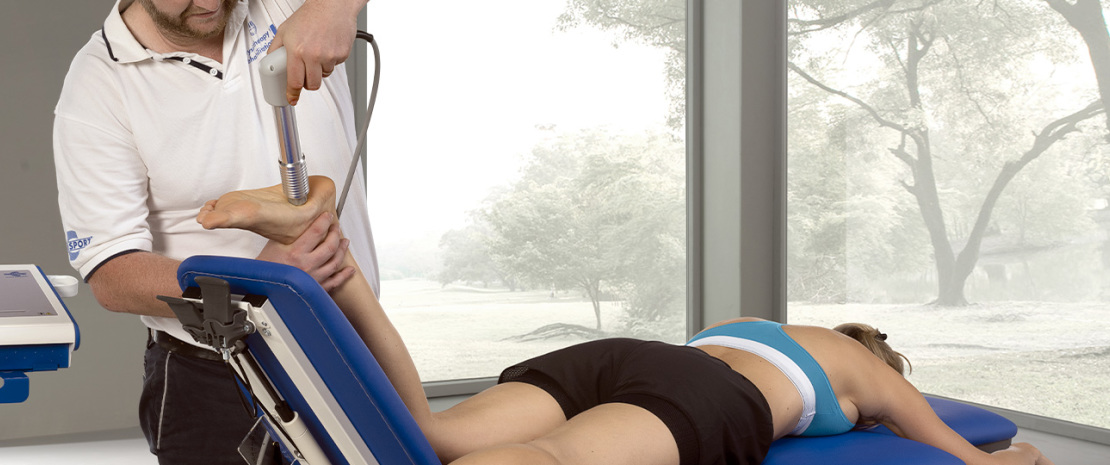
In specific, in the bone tissue osteogenic and vascular reactions were observed, while in soft tissues there were anti-inflammatory, antalgic and vascular reactions.
The spreading of the acoustic wave in the tissues follows the laws of physics of acoustic wave that concern transmission, reflexion and absorption. These laws are linked to the characteristics of the means and are influenced inevitably by differing values of density and impedance of the skin, fat, muscles and bones.
The action mechanism in the muscle-skeletal tissues is very complex and it is still subject to an in-depth research. The shockwaves act in different ways according to the different pathologic tissue they treat (bone, soft tissues, skin). Generally speaking, they stimulate the activation of natural biologic repair processes.
The action mechanism of the shockwaves seems to originate in two main effects:
1. direct physic-mechanical effects: the so-called “cavitation effect” and micro-streaming with consequent creation of new blood vessels that increases local afflux of blood and the production of new cells that speeds up the reparation of micro-lesions and improves tissue trophism;
2. indirect biological effects induce: the reduction of the pain transmission stimulating nerve-ends and freeing substances that regulate its perception; vascularisation that produces bio-molecular modifications.
The main applications are used in the following fields: Orthopedics, Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine.
The shock wave method is the preferred treatment for chronic insertional tendinopathy, characterized by poor vascularization osteotendinea junction, where the physiotherapy treatment (infiltration and laser therapy) has proven ineffective.
Here are the main diseases on which the shock waves are applied:


Introduction - Vacuum therapy - WOK trolley - C.R.E.T. therapy - Shockwave therapy - Laser therapy - High intensity laser therapy - Scanning laser therapy - Low level laser therapy - Electrotherapy - Ultrasound therapy - Combined therapy - Magneto therapy - Radar therapy - Pressotherapy - Traction therapy - TENS units - Thermotherapy
Brochure, Ed. Dec. 2023, English. 60 pages.


